TECHNOLOGY
Making better future with competitive LED technology and expanding into new areaLED APPLICATIONUV sterilization
Ultraviolet sterilization destroys the DNA and RNA of microorganisms, making it impossible to reproduce. Therefore, UV irradiation has a sterilizing and disinfecting effect.
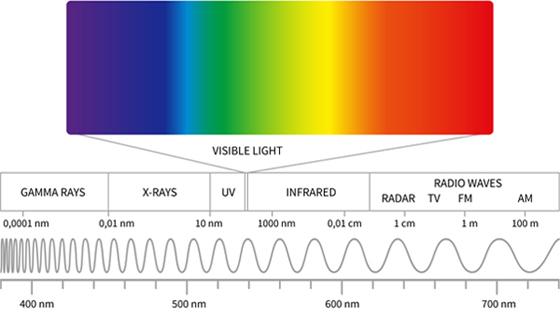

LED APPLICATIONEffect by wavelength

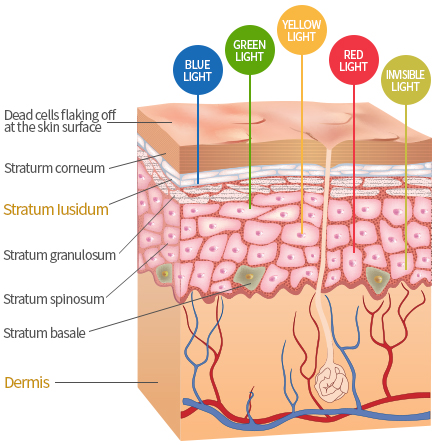
LED APPLICATIONSkin diseases applicable to LED
| Diseases | Effective wavelength | Light intensity |
|---|---|---|
| atopic dermatitis psoriasis |
NBUVB(312±1nm;311-313nm; TLO1); UVA1 (340-400nm; 370-380peak) | NBUVB : 100~200 [ j/cm2 ] UVA1 : 60 [ j/cm2 ] |
| Bacterial/fungal diseases | 380±2nm, 392±1nm |
In vitro studies have been reported that the wavelength band of 380-390nm is effective for Malassezia, a dandruff strain. |
| skin aging; rejuvation | 595±2nm, 630 - 660nm |
Yellow and red are effective. According to Chonnam National University research, yellow is better. |
| acne | 405nm - 415nm (blue LED) 630 ± 8nm (red LED) |
The blue wavelength is effective and red, which has excellent penetration, is also effective. |
| inflammation | 630 - 660nm, 830 ± 3nm |
It may differ depending on the type of inflammation, but IR and RED are effective. |
| Whitening / wound healing | 830 ± 3nm, 850nm |
Both wavelengths are effective, but only cell tests have been proven. |
| Hair loss | 655 ± 5nm or 655 ± 20nm | 35% hair growth observed. |
| erythema | 930nm | Proven at the cell level. Comparative studies with 630~660nm, which are known to have existing effects, are needed. |
LED APPLICATIONPlant growth
LED for plant growth
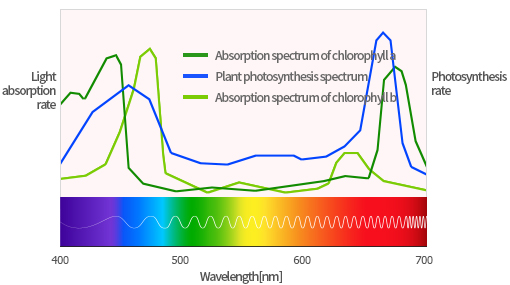
Humans detect light in the range of 380nm to 780nm to distinguish between shades and colors, but plants react physiologically according to the wavelength of light.
It is a light that helps plant growth by using blue light with a wavelength of 400nm~500nm and red light with a wavelength of 640nm~700nm, which helps plant photosynthesis.
It removes light from 500 nm to 640 nm, which does not greatly help plant photosynthesis, and generates only 450 nm and 660 nm light that helps plant growth.
It is a light that can be used as a substitute for sunlight in facility cultivation, and it is not harmful to humans and plants by removing the UV area and the IR area that generates heat.
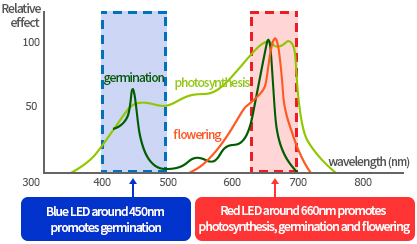
Plant physiological reaction to light wavelength
Plant physiological reaction to light wavelength
Wavelength(nm)
effect
Infrared
IR-A
1400~1000
No effect on photosynthesis. Heat generation due to long wavelength
Visible light
Red
700
Germination inhibition (730 nm), photosynthesis maximum (570 nm)
660
Chlorophyll activity maximum (655nm), germination, leaf embryo formation (660nm)
Reddish yellow
610
Not beneficial for photosynthesis. Pest control(580nm-650nm)
Greenish yellow
510
Some absorption by yellow pigment
Blue
430~440
Maximize photosynthesis, broaden and enlarge leaves, inhibit stem growth
Ultraviolet
UV-A
400~315
Thickening plant leaves, promoting pigmentation, attracting pests
UV-B
280
Immune body formation, functional substance content increase
UV-C
100
Chlorophyll destruction

Humans detect light in the range of 380nm to 780nm to distinguish between shades and colors, but plants react physiologically according to the wavelength of light. It is a light that helps plant growth by using blue light with a wavelength of 400nm~500nm and red light with a wavelength of 640nm~700nm, which helps plant photosynthesis. It removes light from 500 nm to 640 nm, which does not greatly help plant photosynthesis, and generates only 450 nm and 660 nm light that helps plant growth.
It is a light that can be used as a substitute for sunlight in facility cultivation, and it is not harmful to humans and plants by removing the UV area and the IR area that generates heat.




| Wavelength(nm) | effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrared | IR-A | 1400~1000 | No effect on photosynthesis. Heat generation due to long wavelength |
| Visible light | Red | 700 | Germination inhibition (730 nm), photosynthesis maximum (570 nm) |
| 660 | Chlorophyll activity maximum (655nm), germination, leaf embryo formation (660nm) | ||
| Reddish yellow | 610 | Not beneficial for photosynthesis. Pest control(580nm-650nm) | |
| Greenish yellow | 510 | Some absorption by yellow pigment | |
| Blue | 430~440 | Maximize photosynthesis, broaden and enlarge leaves, inhibit stem growth | |
| Ultraviolet | UV-A | 400~315 | Thickening plant leaves, promoting pigmentation, attracting pests |
| UV-B | 280 | Immune body formation, functional substance content increase | |
| UV-C | 100 | Chlorophyll destruction | |
